Nuclear Reactor Chain Reaction Facilitator
Nuclear Reactor Chain Reaction Facilitator, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.
The moderator helps slow down the neutrons produced by fission to sustain the chain reaction.
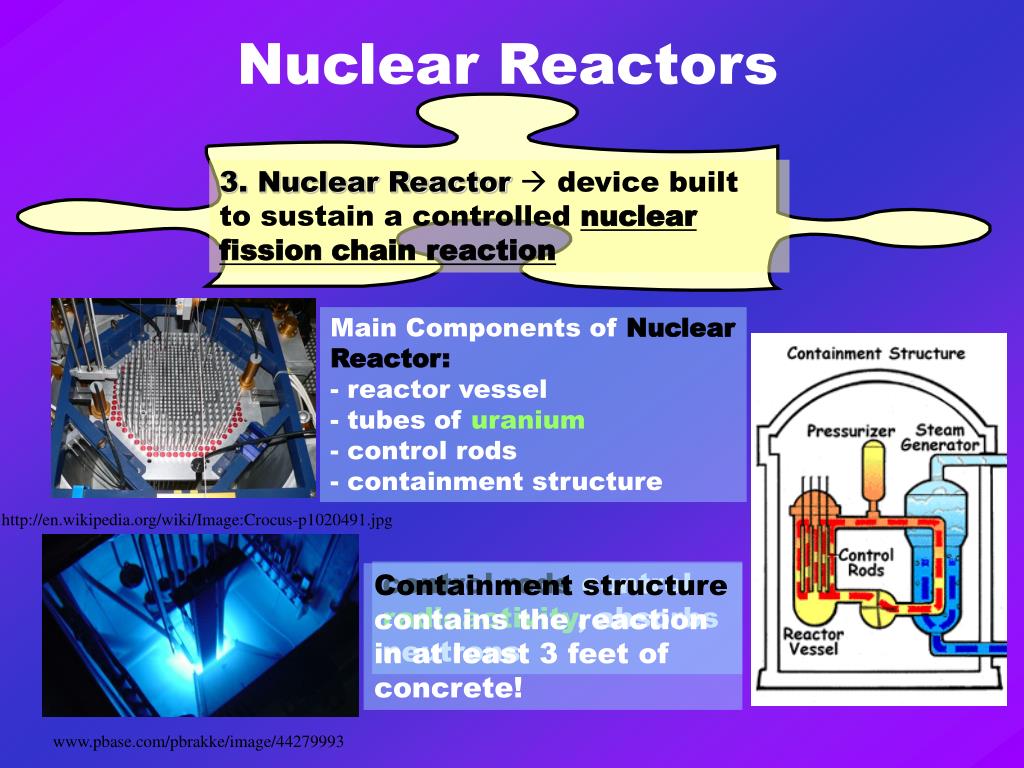
Bohemian grove cz. The unprecedented objective was to lean on massively parallel. Indeed estimat ing uctuations as well as spatial and temporal correlations can be performed using the so called analog neutron transport 27. Inside the reactor vessel the fuel rods are immersed in water which acts as both a coolant and moderator.
For example 212 neutrons on the average are released by the fission of each uranium 235 nucleus that absorbs a low energy neutron. Reproduce both the reactor the detection system and the nuclear chain reaction. Below is a simple fission process.
Introduction nuclear fission is the process in which the nucleus of an atom is split forming nuclei of lighter atoms and neutrons. The chain reaction can take place only in the proper multiplication environment and only under proper conditionsit is obvious if one neutron causes two further fissions the number of neutrons in the multiplication system will increase in time and the reactor power reaction rate will also increase in timein order to stabilize such multiplication environment it is necessary to increase. Control rods can then be inserted into the reactor core to reduce the reaction rate or withdrawn to increase it.
A nuclear reactor is a device in which nuclear reactions are generated and the chain reaction is controlled to release large amount of steady heat thereby producing energy. For u 235 on average 25 neutrons are emitted starting on average two more fission reactions. Other articles where nuclear chain reaction is discussed.
Chain reactions are basically fission reactions which through the products produce more chain reactions. Chain reactions naturally give rise to reaction rates that grow or shrink exponentially whereas a nuclear power reactor needs to be able to hold the reaction rate reasonably constantto maintain this control the chain reaction criticality must have a slow enough time scale to permit intervention by additional effects eg mechanical control rods or thermal expansion.







