Nuclear Reaction In Physics
Nuclear Reaction In Physics, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.

Fission Fusion And Nuclear Energy General Physics Solved Exam Docsity Nuclear Family Journal Nuclear Bomb Core
Most of this energy becomes kinetic energy of the particle or nucleus which moves away at high speed.

Nuclear family journal nuclear bomb core. In any case the bombarding particle must have enough energy to approach the positively charged nucleus to within range of the strong nuclear force. Nuclear reactions such as fission and fusion can be represented using nuclear equations which are similar to chemical equations in chemistry for example. In all nuclear processes the following quantities are conserved.
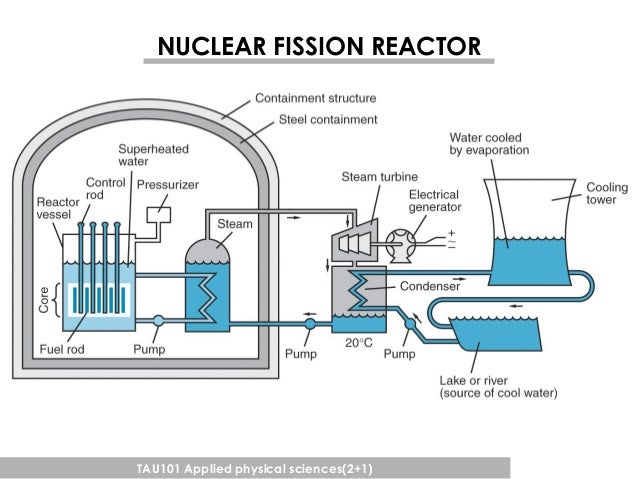
Nuclear reactions nuclear fission nuclear fusion nuclear reactor. A nuclear reaction is a change in the identity or characteristics of an atomic nucleus bombarded with an energetic particle. Most nuclear reactors use a chain reaction to induce a controlled rate of nuclear fission in fissile material releasing both energy and free neutrons.
The bombarding particle may be an alpha particle a gamma ray photon a neutron a proton or a heavy ion. Induced nuclear reactions occur when a nucleus changes as a result of being struck by a particle. Such an equation represents a nuclear reaction.
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry a nuclear reaction is semantically considered to be the process in which two nuclei or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle collide to produce one or more new nuclidesthus a nuclear reaction must cause a transformation of at least one nuclide to another. A nuclear reaction involves the rearrangement of the nuclear constituents. This nuclear is change is represented by the following equation.
In nuclear and particle physics the energetics of nuclear reactions is determined by the q value of that reaction. Significance the energy released in this decay is in the mev range many times greater than chemical reaction energies. The nucleus can be left in an excited state to later emit photons.
Nuclear reaction change in the identity or characteristics of an atomic nucleus induced by bombarding it with an energetic particle. The bombarding particle may be an alpha particle a gamma ray photon a neutron a proton or a heavy ion. Proton number charge mass energy.
Learn more about nuclear reactions in this article. The energy carried away by the recoil of the nucleus is much smaller due to its relatively large mass. A nuclear reaction is considered to be the process in which two nuclear particles two nuclei or a nucleus and a nucleon interact to produce two or more nuclear particles or rays thus a nuclear reaction must cause a transformation of at least one nuclide to another.
The above equation represents a fission reaction in which a uranium nucleus is hit with a neutron and splits into two smaller nuclei a strontium nucleus and a xenon nucleus releasing two neutrons in the process. While studying radioactivitywe have seen that an a particle is emitted from radium 226 and radon 222 is obtained. The q value of the reaction is defined as the difference between the sum of the masses of the initial reactants and the sum of the masses of the final products in energy units usually in mev.