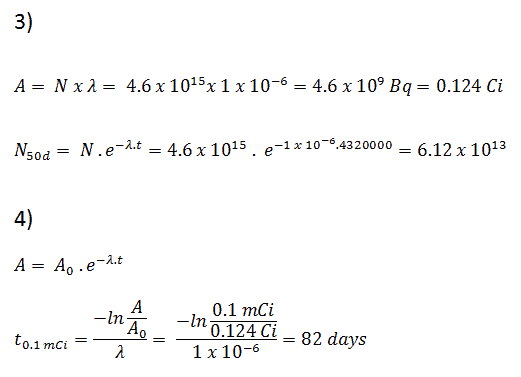Nuclear Reaction For Beta Decay
Nuclear Reaction For Beta Decay, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.
In a nuclear reactor occurs especially the b decay because the common feature of the fission products is an excess of neutrons see nuclear stability.

Nuclear waste from japan. The production of beta particles is termed beta decay. Write a nuclear decay reaction that produces the nucleus. Natural nuclear decay reactions examples tutorials on nuclear reactions complete beta decay reaction of 210 85 at in nuclear reactions is the charge conserved properties of natural radioactivity graph natural radioactive reaction properties of natural radioactivity radioactive decay number of protons electrons and neutrons in 21085 at natural.
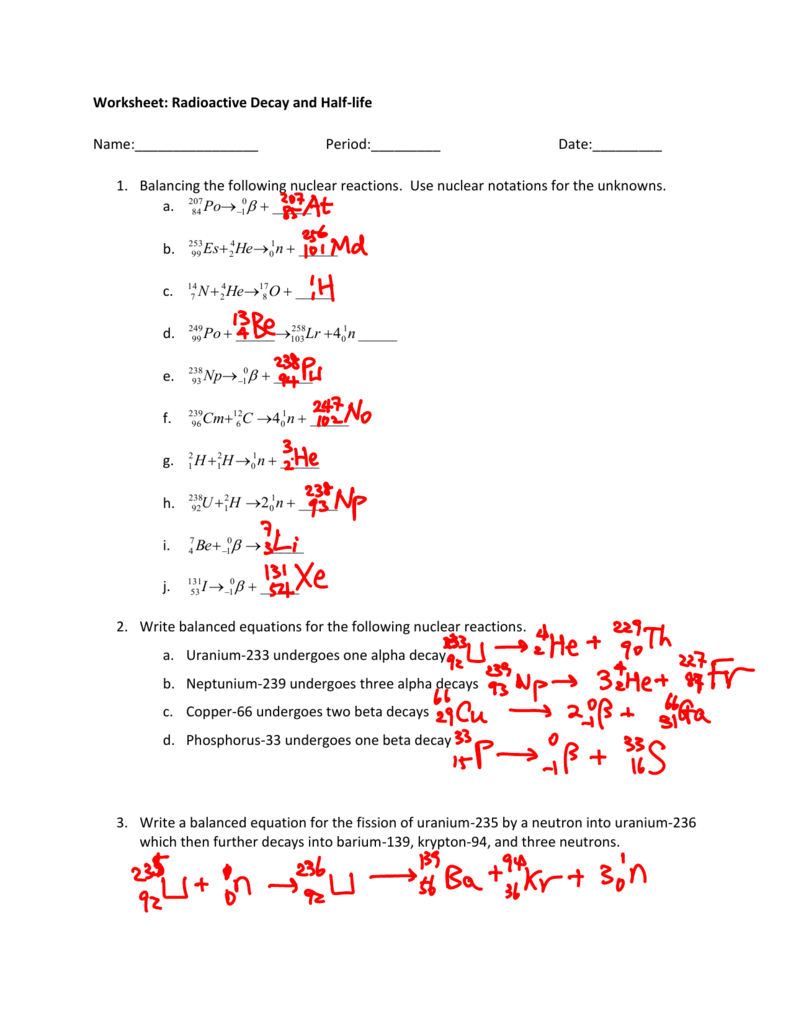
Beta decay is the loss of an electron from the nucleus of an atom. Or conversely a proton is converted into a. The atomic numbers and mass numbers in a nuclear equation must be balanced.
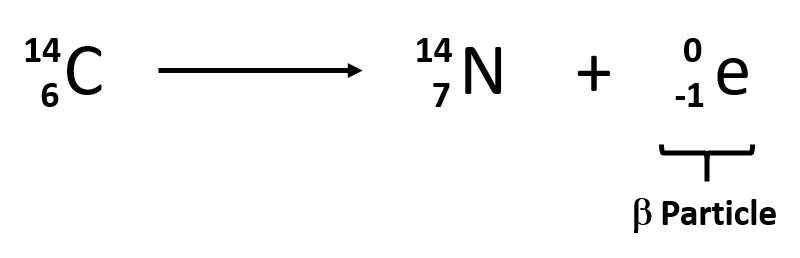
Nuclear reactions the high flux of antineutrinos is required similar to those present in nuclear reactors. During beta decay a proton in the nucleus of the unstable atom is changed into a neutron or vice versa. For the b decay of iodine 131 we have.
In any nuclear equation the sum of the subscripts atomic numbers z and the sum of the superscripts atomic masses m must be equal on each side of the equation. There are two forms of beta decay the electron decay b decay and the positron decay b decay. One of the three main types of radioactive decay is known as beta decay b decay.
Electron capture known also as inverse beta decay is sometimes included as a type of beta decay because the basic nuclear process mediated by the weak interaction is the same. Protons and neutrons are made up of quarks. That neutron may be thought of as a combination of a beta particle negative charge with a proton positive charge.
Most nuclear reactions emit energy in the form of gamma rays. The parent nuclide is a major waste product of reactors and has chemistry similar to calcium so that it is concentrated in bones if ingested. A nuclear reaction is one that changes the structure of the nucleus of an atom.
B decay is a process in which a nucleus emits an electron. The nuclear symbol for a b particle is colorwhiteltext 10e. In this process a proton rich nucleus can also reduce its nuclear charge by one unit by absorbing an atomic electron.
The two most common modes of natural radioactivity are alpha decay and beta decay. Radioactive decay involves the spontaneous splitting of heavy unstable isotopes. In nuclear physics beta decay b decay is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle fast energetic electron or positron is emitted from an atomic nucleus transforming the original nuclide to an isobarfor example beta decay of a neutron transforms it into a proton by the emission of an electron accompanied by an antineutrino.
When an aqueous solution of cdcl 2 is placed into a nuclear reactor antineutrinos react with the protons of water in the reaction 4109. Nuclear beta decay involves the conversion of one nucleon into another. In beta decay a high energy electron called a beta particle is emitted from a neutron in the nucleus of a radioactive atom.
Inverse beta decay electron capture.