Nuclear Reaction And Radioactive Decay
Nuclear Reaction And Radioactive Decay, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.
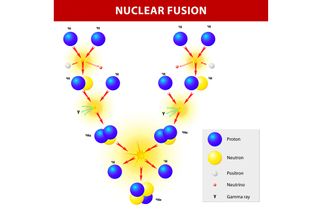
Ch103 Chapter 3 Radioactivity And Nuclear Chemistry Chemistry Nuclear Fusion Definition Chemistry Nuclear Power Disadvantages And Advantages
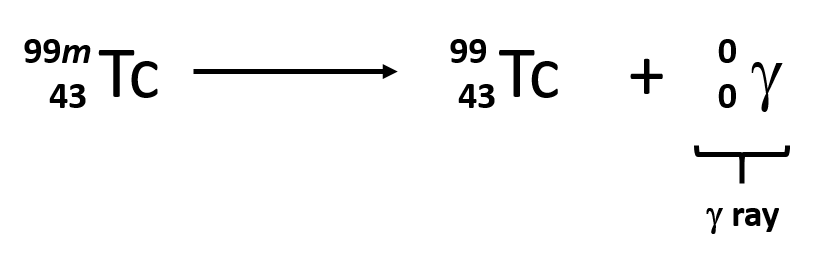
Radioactivity Law Of Radioactive Decay Decay Rate Half Mean Life Q A Nuclear Fusion Definition Chemistry Nuclear Power Disadvantages And Advantages
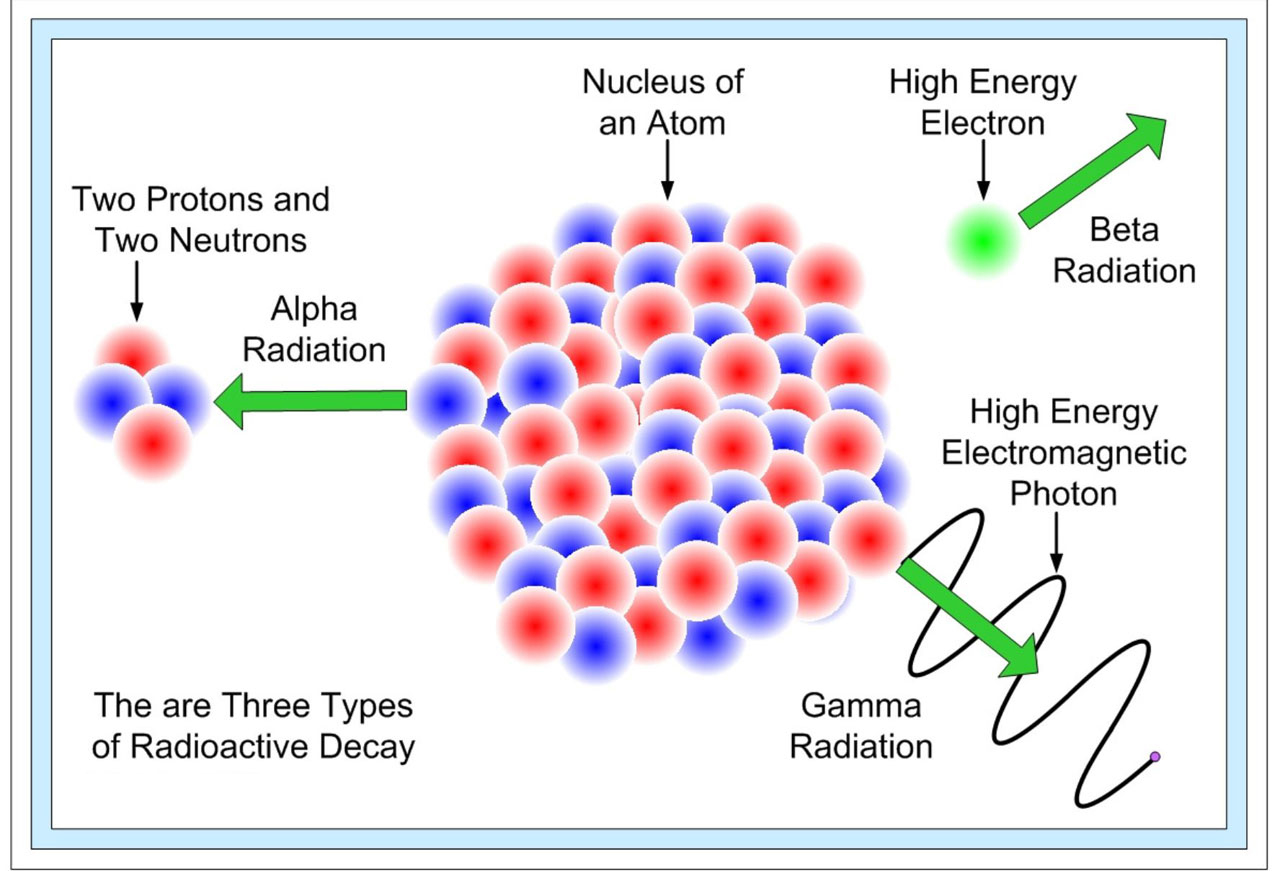
Radioactive substances give off three types of radiation.
Nuclear fusion definition chemistry nuclear power disadvantages and advantages. The nucleus is made stable by the emission of particles from the decaying nucleus. Well the mass number and the charge are the two things that are always conserved in a nuclear reaction in every nuclear reaction. Radioactive decay happens when the nucleus is unstable due to the number of protons and neutrons within the nucleus.
Alright so whats conserved in a nuclear reaction. In chemical reactions the nuclei of the atoms from the reactants to the products is unchanged. Nuclear decay radioactive decay occurs when an unstable atom loses energy by emitting ionizing radiationradioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms in that according to quantum theory it is impossible to predict when a particular atom will decay.
Well theyre reactions between nuclei. Every single radioactive decay every single nuclear collision every single nuclear reaction. What are nuclear reactions.
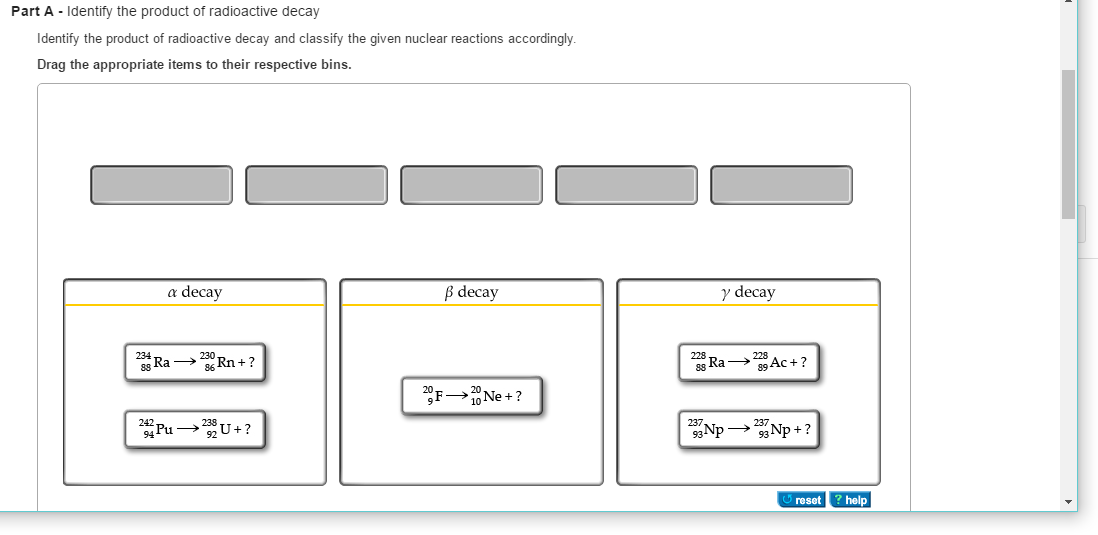
In nuclear reactions the protons and neutrons are rearranged in the nucleus of the atom to form new elements. Alpha particles beta particles and gamma rays. Radioactive decay also known as nuclear decay radioactivity radioactive disintegration or nuclear disintegration is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiationa material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactivethree of the most common types of decay are alpha decay beta decay and gamma decay all of which involve emitting one or more particles.
Nuclear decay reactions occur spontaneously under all conditions and produce more stable daughter nuclei whereas nuclear transmutation reactions are induced and form a product nucleus that is more massive than the starting material. Here is the equation for the alpha decay of radon 219 into polonium. What is radioactive decay notation of nuclear reactions radioactive decays source.
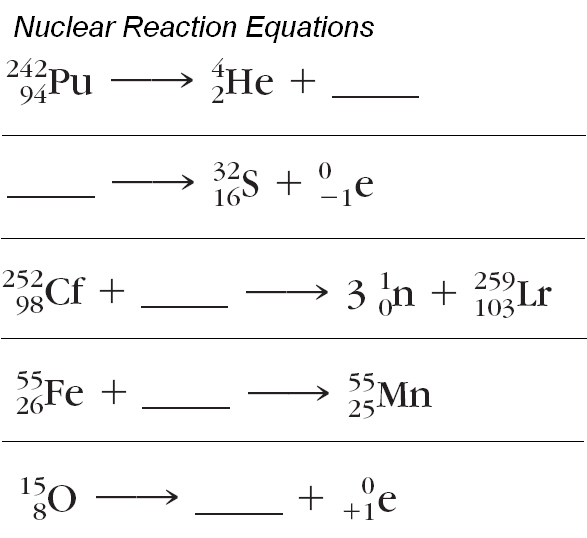
Nuclear reaction and radioactive decay what properties are conserved in all particle reactions and decays i2 nuclear reaction examples is charge conserved in a nuclear decay radioactive decay natural example of the radioactive reaction particle reactions proton positron to neutron. When a radioactive atom emits an alpha particle the mass number decreases by four and the atomic number drops by two.
Solved When A Nucleus Undergoes Radioactive Decay A Daug Chegg Com Nuclear Fusion Definition Chemistry Nuclear Power Disadvantages And Advantages