Nuclear Radiation Formula
Nuclear Radiation Formula, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.
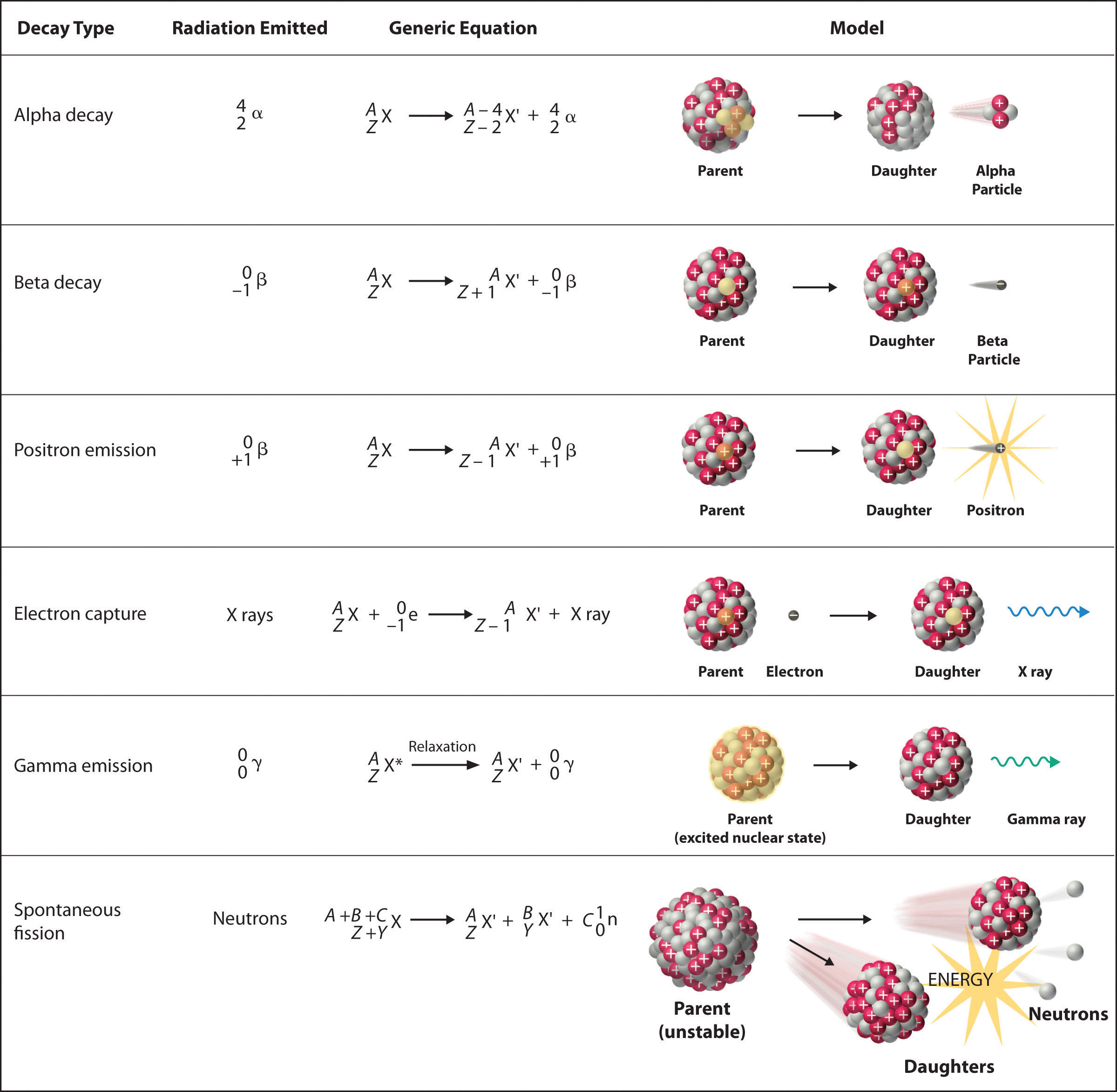
The sum of the mass numbers of the reactants equals the sum of the mass numbers of the products.

Illegal weapon punjabi lyrics in english. Atoms are made up of a positively charged nucleus. The interaction of radiation with the organic compounds occurs at the molecular level. The atomic numbers and mass numbers in a nuclear equation must be balanced.
The radioactive decay law states that the probability per unit time that a nucleus will decay is a constant independent of time. Equivalent dose is based on the absorbed dose to an organ adjusted to account for the effectiveness of the type of radiationequivalent dose is given the symbol h tthe si unit of h t is the sievert sv or but rem roentgen equivalent man is still commonly used 1 sv 100 rem. The formula for radioactive decay is calculated using the initial quantity of substance and half lifetime.
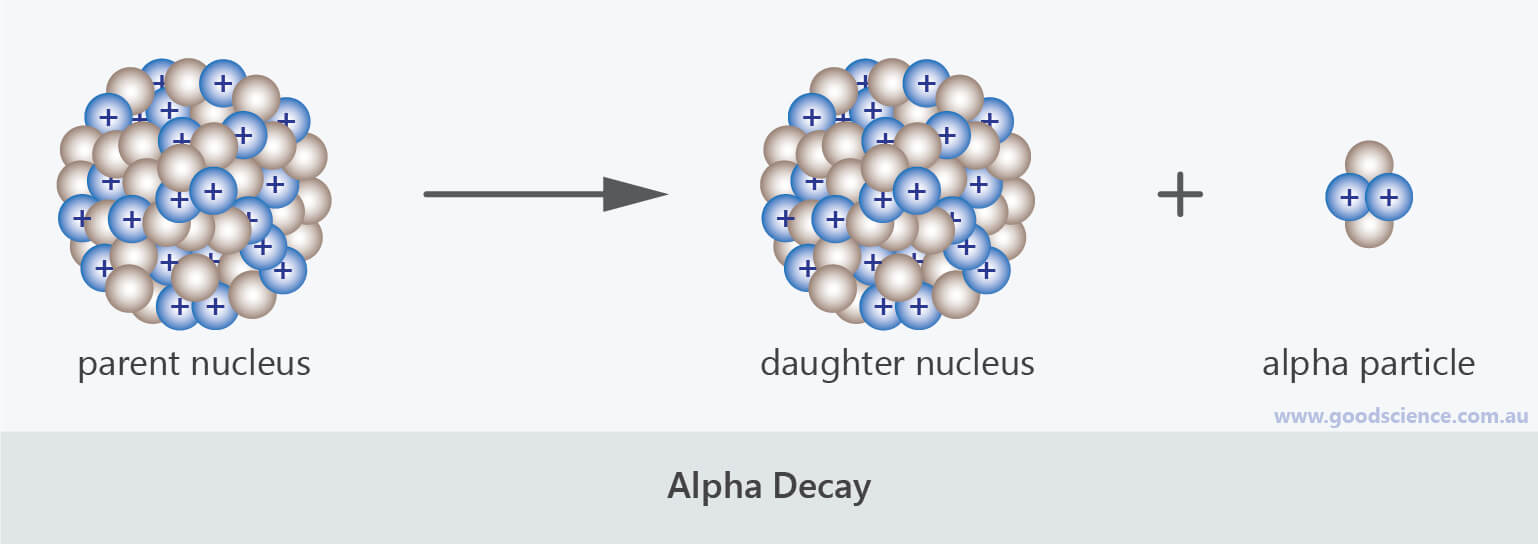
This constant probability may vary greatly between different types of nuclei leading to the many different observed decay rates. The following apply for the nuclear reaction. The two most common modes of natural radioactivity are alpha decay and beta decay.
Protons and neutrons are made up of quarks. Nuclear equations represent the reactants and products in radioactive decay nuclear fission or nuclear fusion. Instead of chemical equations where it shows the different number of elements is conserved in a reaction in a nuclear reaction the atomic mass and proton number are conserved.
A balanced nuclear reaction equation indicates that there is a rearrangement during a nuclear reaction but of subatomic particles rather than atoms. Decay law equation formula. This constant is called the decay constant and is denoted by l lambda.
Nuclear reactions also follow conservation laws and they are balanced in two ways. A nuclear reaction is one that changes the structure of the nucleus of an atom. Highlight the important terms phrases in each dot point.
That is the organic molecule in a ground energy. Design a powerpoint presentation on nuclear radiation with each slide. Nuclear radiation slide 2.
Most nuclear reactions emit energy in the form of gamma rays. In these examples the sum of the masses top and the sum of the proton numbers bottom are the same on. The spontaneous breakdown of an atomic nucleus of a radioactive substance causing the emission of radiation from the nucleus is known as radioactive decay.
Radioactive decay also known as nuclear decay radioactivity radioactive disintegration or nuclear disintegration is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiationa material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactivethree of the most common types of decay are alpha decay beta decay and gamma decay all of which involve emitting one or more particles. In the centre of mass frame where a and b are the initial species about to collide c is the final species and r is the resonant state. You may copy and paste the points from this page.
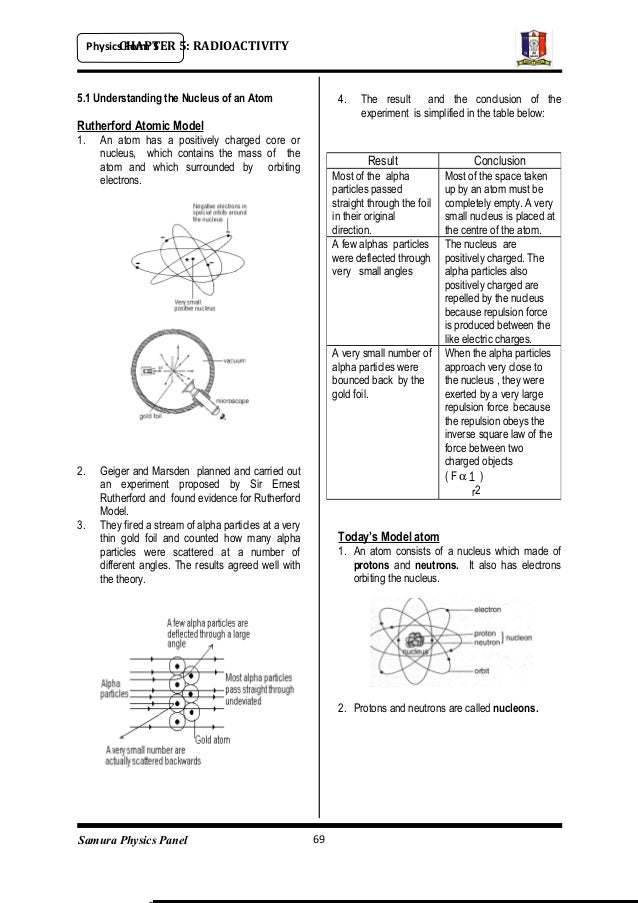
Describe the nuclear model of the atom. Equivalent dose symbol h t is a dose quantity calculated for individual organs index t tissue.