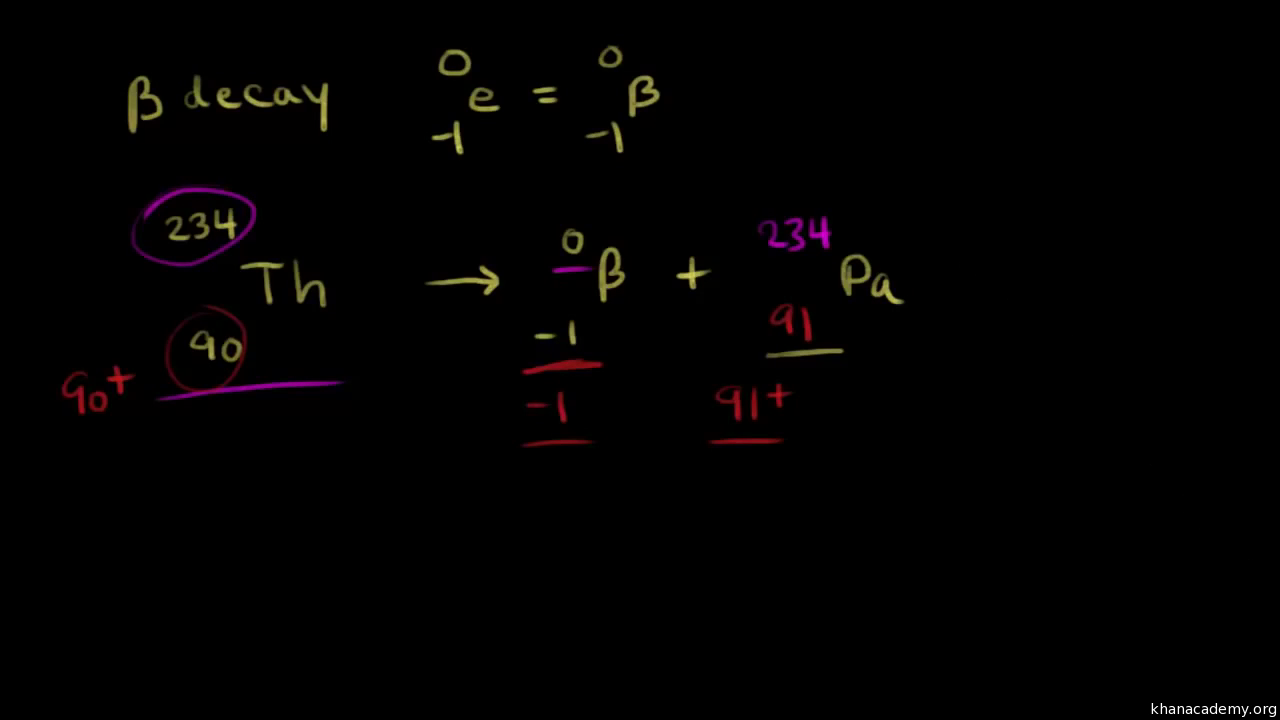Gamma Decay Nuclear Reaction
Gamma Decay Nuclear Reaction, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.
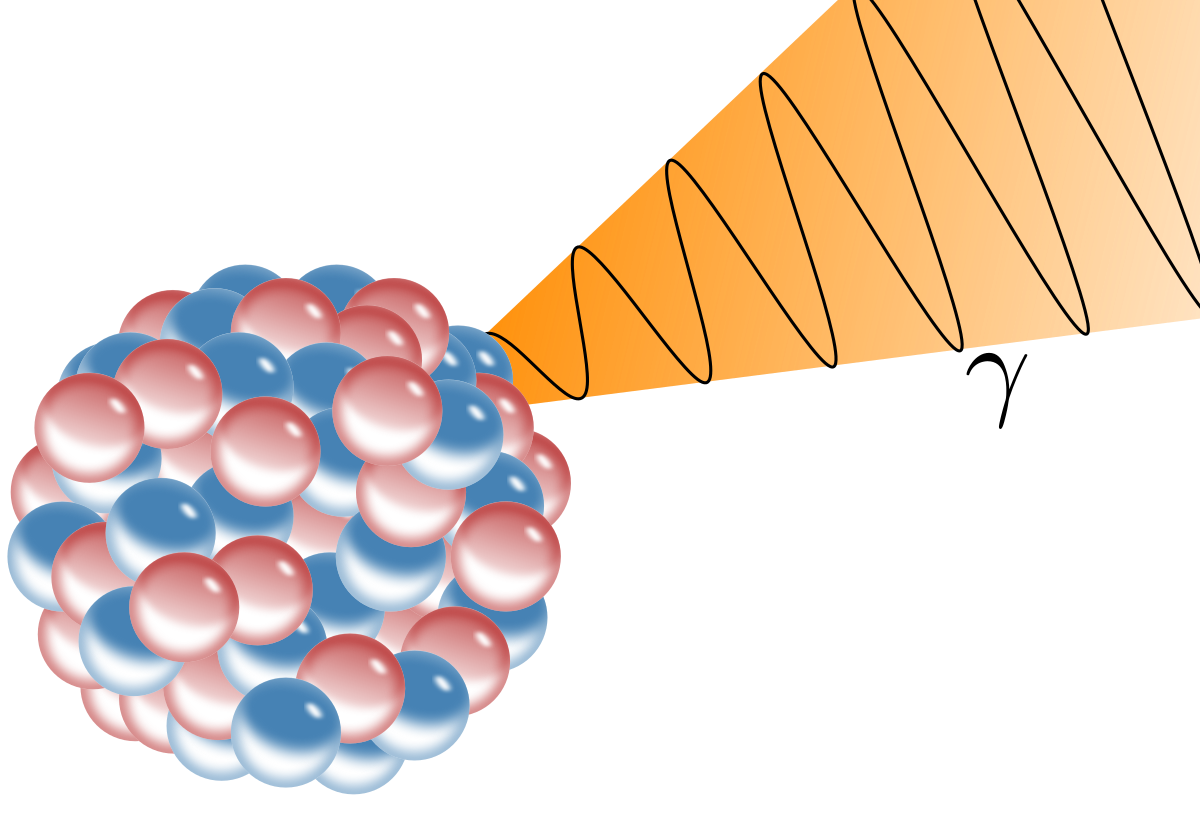
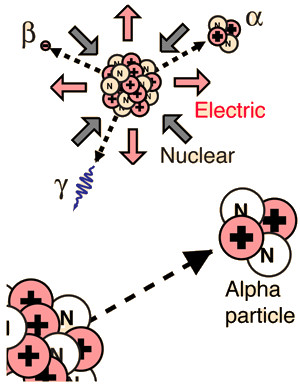
The unstable nuclei that undergo gamma decay are the products either of other types of radioactivity alpha and beta decay or of some other nuclear process such as neutron capture in a nuclear reactorthese product nuclei have more than their normal energy which they lose in discrete amounts as gamma ray photons until they reach their lowest energy level or ground state.

In the nuclear reaction xn alpha. Gamma decay is the third type of radioactive decay. 94 240 pu 92 236 u 2 4 he. A photon is a massless particle with a very small wavelength.
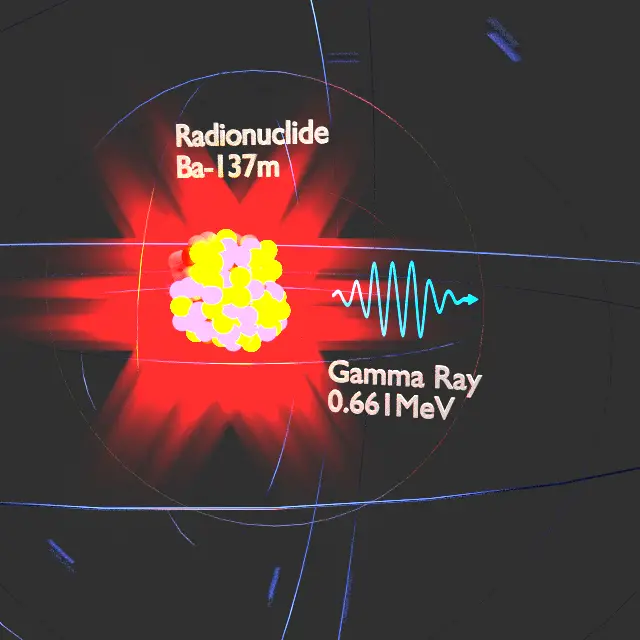
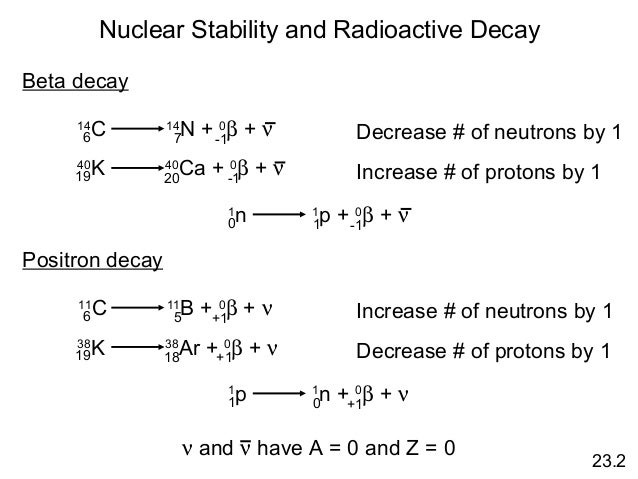
It differs from alpha and beta decay in that it does not involve a change in the chemical isotope. During gamma decay the energy of the parent atom is changed by the emission of a photon. Nuclear reactions and radioactive decay result in the emission of gamma rays with discrete energies which provide a fingerprint that can uniquely identify specific elements in the surface.
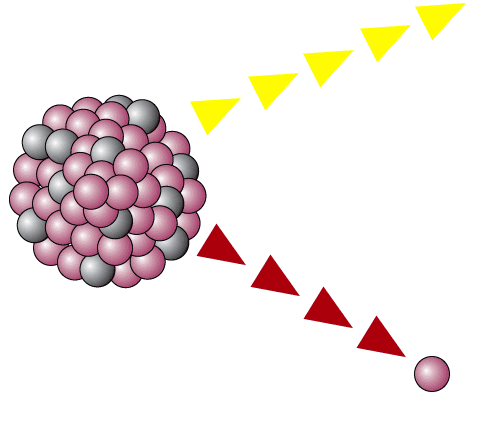
Most of nuclear reactions produce extremely unstable nuclei that decay as soon as they are formed in nuclear reactions half life less than 10 11 s and are not generally classified as nuclear isomers. As was written gamma decay may follow nuclear reactions such as neutron capture nuclear fusion or nuclear fission. This could lead to serious problems for.
Most nuclear reactions emit energy in the form of gamma rays. Typically radiative decay proceeds the aforementioned particle decay as the resulting daughter nucleus resides in an energetic excited state 12analogous to the production x rays a gamma photon is produced as the nucleus. The atomic numbers and mass numbers in a nuclear equation must be balanced.
Protons and neutrons are made up of quarks. Natural nuclear decay reactions examples tutorials on nuclear reactions complete beta decay reaction of 210 85 at in nuclear reactions is the charge conserved. After gamma decay atomic number and mass number of nucleus are conserved.
Nuclear reactions alpha beta and gamma decay nuclear reactions alpha beta and gamma decay cs 42 cs 43 state what is meant by alpha beta and gamma decay. The two most common modes of natural radioactivity are alpha decay and beta decay. Most of nuclear reactions produce extremely unstable nuclei that decay as soon as they are formed in nuclear reactions half life less than 10 11 s and are not generally classified as nuclear isomers.
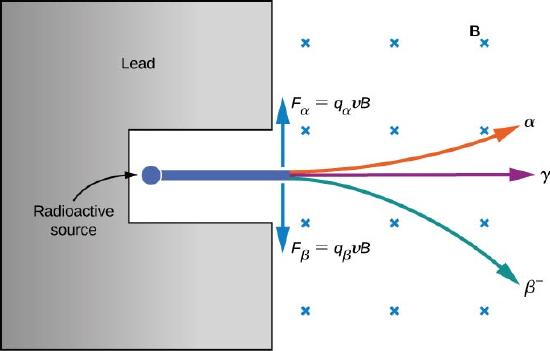
A nuclear reaction is one that changes the structure of the nucleus of an atom. The resulting energy of the daughter atom is lower than the parent atom. The energy of the photon is large and therefore has a large penetration effect.