Energy Released In Nuclear Reaction Formula
Energy Released In Nuclear Reaction Formula, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.
To illustrate suppose two nuclei labeled x and a react to form two other nuclei y and b denoted x a y b.
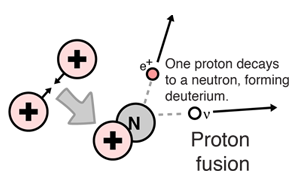
Illegal weapon song. Using einsteins mass energy equivalence formula e mc2 the amount of energy released can be. Sometimes if a nucleus interacts with another nucleus or particle without changing the nature of any nuclide the process. A large amount of energy is released by nuclear fusion reactionsit seems that for power generation the deuterium tritium reaction is the most practical but it provides most of the energy to the released neutron.
In a nuclear reaction the total relativistic energy is conserved. Nuclear fusion process by which nuclear reactions between light elements form heavier elements up to iron. The particles a and b are often nucleons either protons or neutrons but in general can be any nuclei.
Disintegration energy is the energy released during radioactive decay. Energy released in fusion reactions. Because the energy changes in nuclear reactions are so large they are often expressed in kiloelectronvolts 1 kev 10 3 ev megaelectronvolts 1 mev 10 6 ev and even gigaelectronvolts 1 gev.
A nuclear reaction is considered to be the process in which two nuclear particles two nuclei or a nucleus and a nucleon interact to produce two or more nuclear particles or rays thus a nuclear reaction must cause a transformation of at least one nuclide to another. Energy is released in a nuclear reaction if the total mass of the resultant particles is less than the mass of the initial reactants. In cases where the interacting nuclei belong to elements with low atomic numbers eg hydrogen atomic number 1 or its isotopes deuterium and tritium substantial amounts of energy are released.
During a nuclear reaction such as a fission or fusion reaction the mass accounted for by the nuclear binding energy is released in accordance with the equation e mc 2 energy mass times the square of the speed of light. The missing rest mass must therefore reappear as kinetic energy released in the reaction. That is problematic because it is harder to extract the energy from neutrons compared to charged particles.
To simplify the products formed in nuclear fission and nuclear fusion always have a lower mass than the reactants. The energy released in this nuclear reaction is more than 100000 times greater than that of a typical chemical reaction even though the decay of 14 c is a relatively low energy nuclear reaction. The vast energy potential of nuclear fusion was first exploited in thermonuclear.







