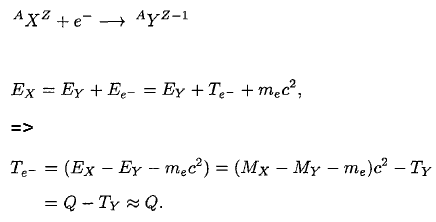Conservation Laws In Nuclear Reactions
Conservation Laws In Nuclear Reactions, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.
Conservation laws in nuclear reactions.
Ordained minister wedding ceremony. Strictly speaking mass is not a conserved quantity. Additional conservation laws not anticipated by classical physics are are electric charge lepton number and baryon number. Sometimes if a nucleus interacts with another nucleus or particle without.
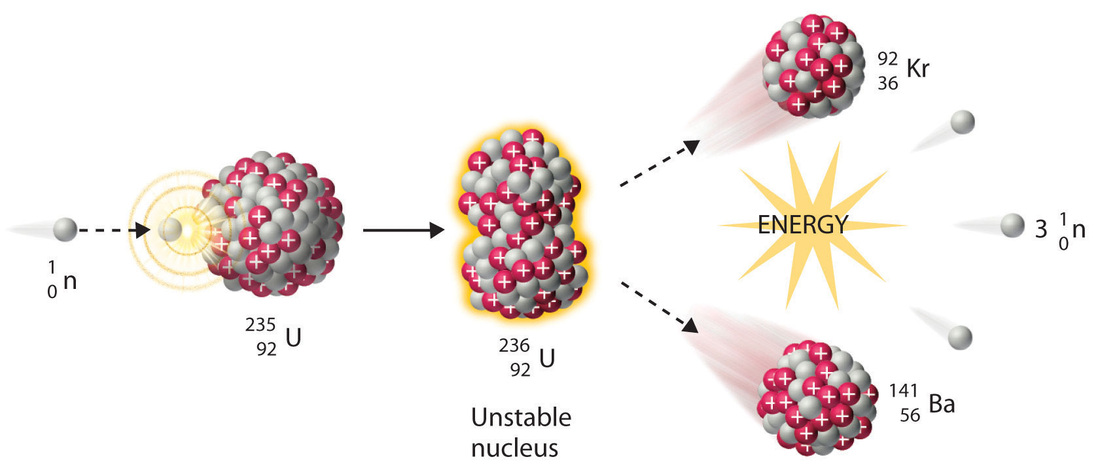
A nuclear reaction is considered to be the process in which two nuclear particles two nuclei or a nucleus and a nucleon interact to produce two or more nuclear particles or rays thus a nuclear reaction must cause a transformation of at least one nuclide to another. However except in nuclear reactions the conversion of rest mass into other forms of. Conservation of energy in nuclear reactions.
According to this law mass and energy are equivalent and convertible one into the other. In analyzing nuclear reactions we have to apply the general law of conservation of mass energy. Sometimes if a nucleus interacts with another nucleus or particle without.
In this section we explore the major modes of nuclear decay. Nuclear decay gave the first indication of the connection between mass and energy and it revealed the existence of two of the four basic forces in nature. It is one of the striking results of einsteins theory of relativitythis equivalence of the mass and energy is described by einsteins famous formula e mc 2.
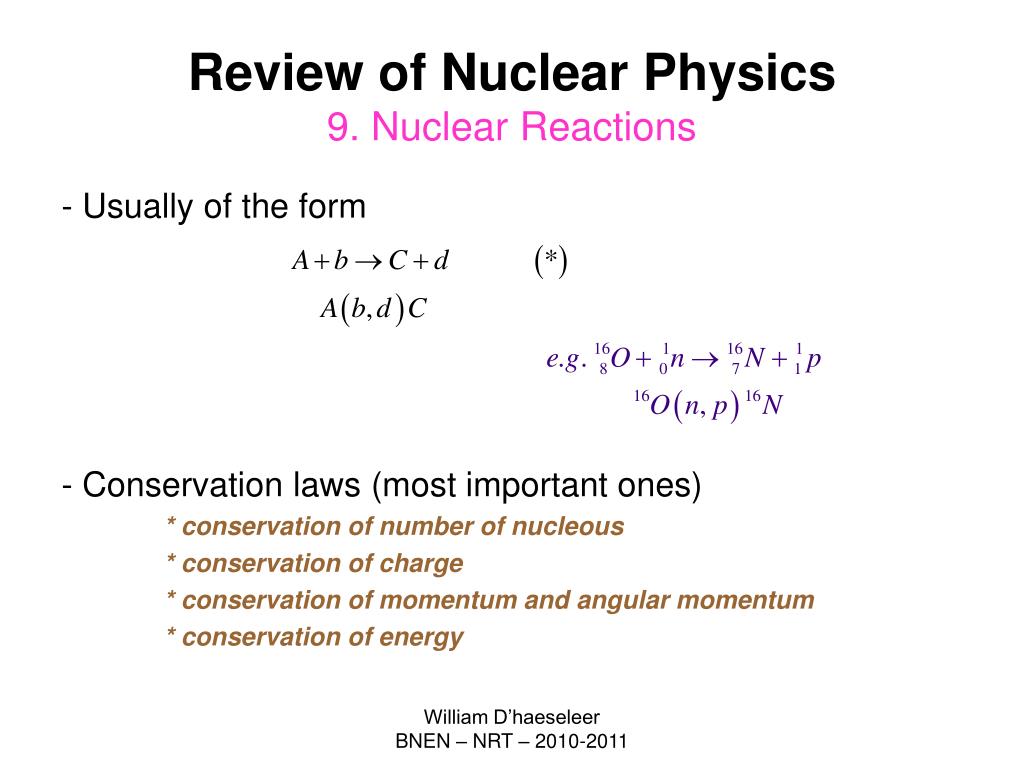
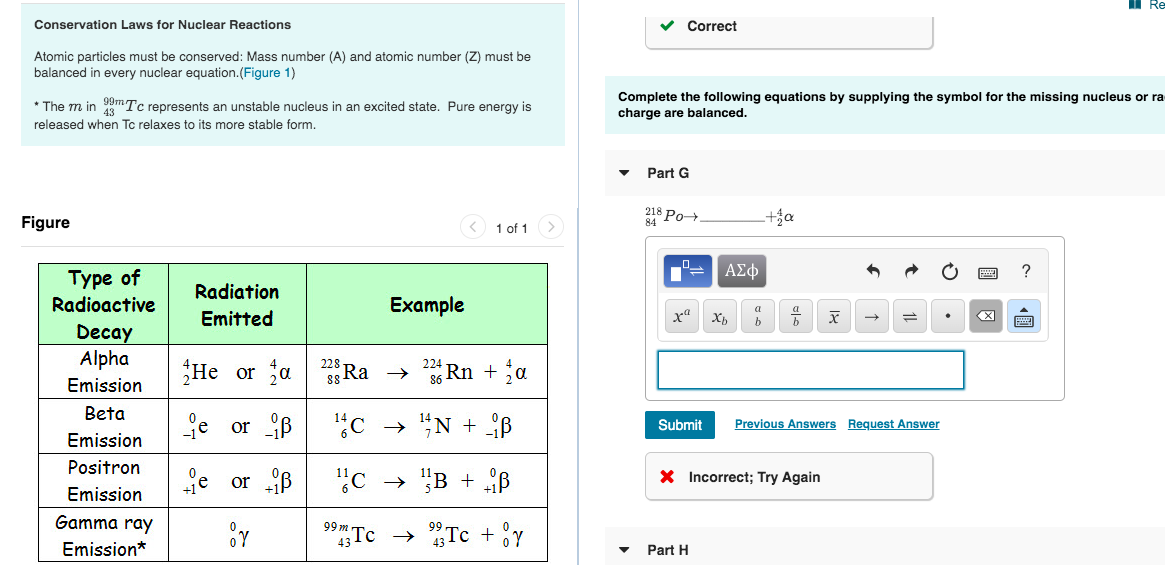
Nuclear reactions are subject to classical conservation laws for charge momentum angular momentum and energy including rest energies. A nuclear reaction is considered to be the process in which two nuclear particles two nuclei or a nucleus and a nucleon interact to produce two or more nuclear particles or rays. Conservation of mass implies that matter can be neither created nor destroyedie processes that change the physical or chemical properties of substances within an isolated system such as conversion of a liquid to a gas leave the total mass unchanged.
Nuclear reactions are subject to classical conservation laws for charge momentum angular momentum and energy including rest energies. Conservation laws in nuclear reactions. The combination of charge conjugation c parity p and time reversal t is considered to be a fundamental symmetry operation all physical particles and interactions appear to be invariant under this combination.
A nuclear reaction is considered to be the process in which two nuclear particles two nuclei or a nucleus and a nucleon interact to produce two or more nuclear particles or rays thus a nuclear reaction must cause a transformation of at least one nuclide to another. Conservation laws in nuclear reactions. Conservation laws in nuclear reactions in analyzing nuclear reactions we apply the many conservation laws.
In analyzing nuclear reactions we apply the many conservation laws.