Radiation Nuclear X Ray
Radiation Nuclear X Ray, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.
Radiation Nuclear Radiation Ionizing Radiation Health Effects World Nuclear Association Nuclear Fission Diagram Nuclear Weapons In Cold War

Radiation X Ray Tube Nuclear Physics Radioactive Decay Png 952x1024px Radiation Area Diagram Electromagnetic Radiation Gamma Nuclear Fission Diagram Nuclear Weapons In Cold War
X rays are also called radiation.

Nuclear fission diagram nuclear weapons in cold war. An x ray or x radiation is a penetrating form of high energy electromagnetic radiationmost x rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz 310 16 hz to 310 19 hz and energies in the range 124 ev to 124 kevx ray wavelengths are shorter than those of uv rays and typically longer than those of. It just depends on how you use it. X rays also known as x radiation refers to electromagnetic radiation no rest mass no charge of high energiesx rays are high energy photons with short wavelengths and thus very high frequency.
Ionizing radiation can damage dna and although your cells repair most of the damage they sometimes do the job imperfectly leaving small areas of. There are many kinds of radiation that move in waves most of them very familiar to you like radio waves visible light and x rays. Radiation can also be described as non ionizing or ionizing.
Photons are categorized according to the energies from low energy radio waves and infrared. Radiation particularly associated with nuclear medicine and the use of nuclear energy along with x rays is ionizing radiation which means that the radiation has sufficient energy to interact with matter especially the human body and produce ions ie. X rays are a form of energy similar to light and radio waves.
They are all part of the electromagnetic spectrum. X ray machines some types of sterilization equipment and nuclear power plants all use nuclear radiation but so do nuclear weaponsnuclear materials that is substances that emit nuclear radiation are fairly common and have found their way into our normal vocabularies in many. Other man made sources include nuclear power generators consumer products like smoke detectors and televisions and industrial sources.
Unlike light waves x rays have enough energy to pass through your body. Nuclear radiation can be both extremely beneficial and extremely dangerous. Using radiation such as x rays doctors can make quick non intrusive and accurate diagnoses of a patients organs.
When the gamma rays undergoes photoelectric effect in surrounding materials for example lead shield the outgoing x ray can be captured again by the detector. Radiation is simply the transmission of energy from a source via waves or particles. The radiation you get from x ray ct and nuclear imaging is ionizing radiation high energy wavelengths or particles that penetrate tissue to reveal the bodys internal organs and structures.
This interaction between ionizing radiation and. This gives an characteristic x ray peak with an energy depending on the material it came from. It can eject an electron from an atom.
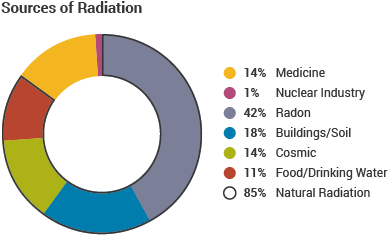
The radiation frequency is key parameter of all photons because it determines the energy of a photon. In case of lead the characteristic x ray energies is in the 72 84 kev range. In comparison to natural environmental radiation man made sources of ionizing radiation contribute very little to the total annual.
The largest source of man made ionizing radiation is medical x rays.

What You Should Know About Radiation And Nuclear Medicine Fred Fahey Dsc Snmmi Nuclear Fission Diagram Nuclear Weapons In Cold War