Nuclear Reaction Heat
Nuclear Reaction Heat, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.
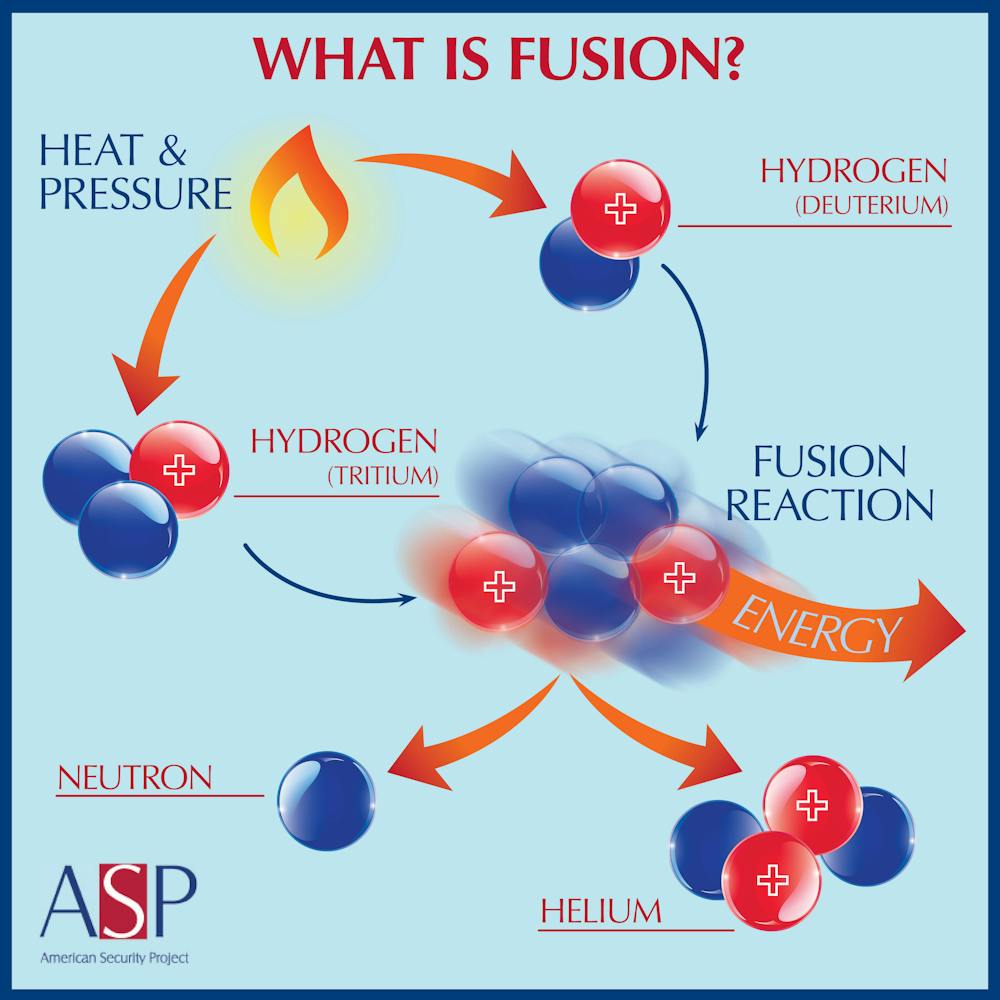
If a nucleus interacts with another nucleus or particle and they then separate without.
Bohemian grove di san francisco. In order to ensure the nuclear reaction takes place at the right speed reactors have systems that accelerate slow or shut down the nuclear reaction and the heat it produces. In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry a nuclear reaction is semantically considered to be the process in which two nuclei or a nucleus and an external subatomic particle collide to produce one or more new nuclidesthus a nuclear reaction must cause a transformation of at least one nuclide to another. It is the source of 60 of radioactive release risk worldw ide.
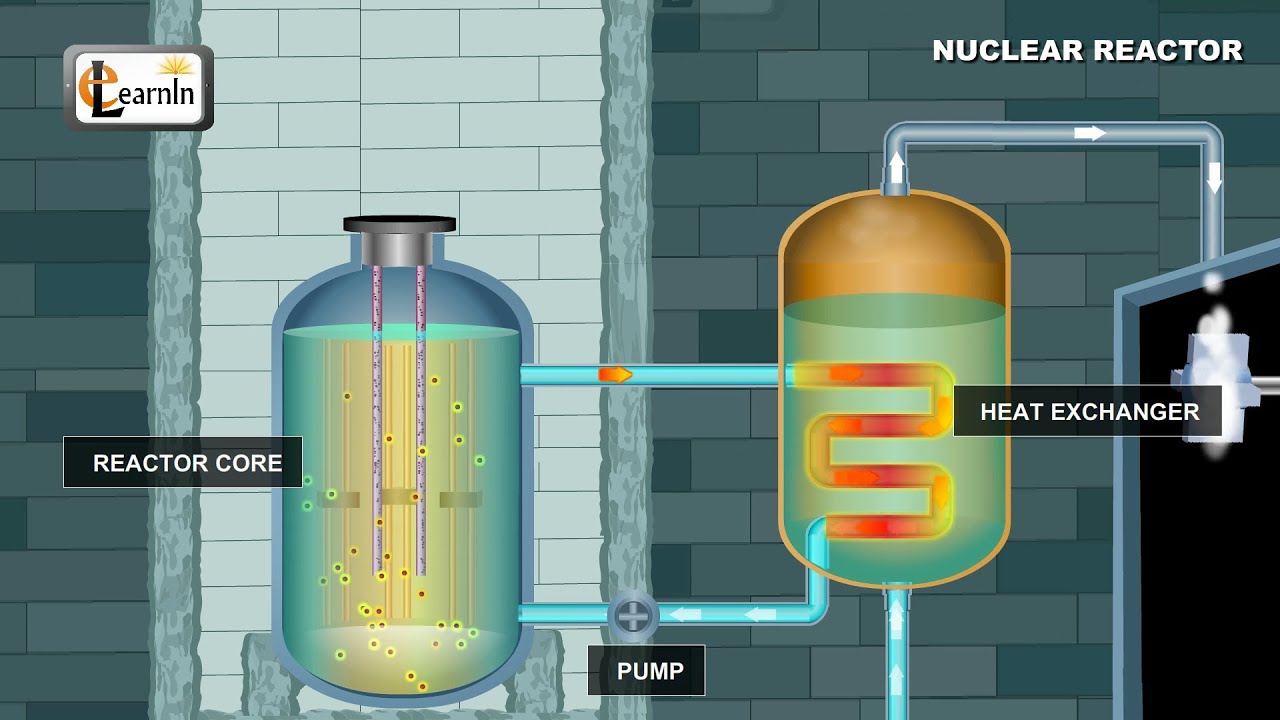
With more than 450 commercial reactors worldwide including 95 in the united states nuclear power continues to be one of the largest sources of reliable. Decay heat is the principal reason of safety concern in light water reactors lwr. Decay heat is the heat produced by the decay of radioactive fission products after a nuclear reactor has been shut down.
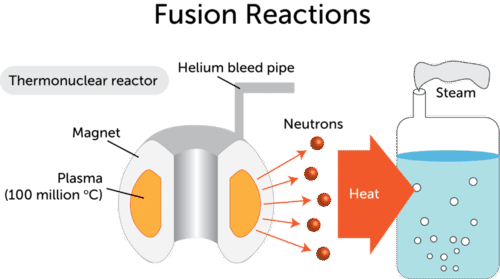
In nuclear reactors there is a direct proportionality between the neutron flux and the reactor thermal powerthis proporcionality is determined by the fission reaction rate per unit volume rr f sthe fission reaction rate within a nuclear reactor is controlled by several factors. Presently the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by nuclear fission of uranium. That heat is used to make steam that spins a turbine to create electricity.
This heat can then be used to generate steam which drives turbines for electricity production.
/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/31117007/european_space_agency.0.jpg)