Nuclear Radiation Chemistry Definition
Nuclear Radiation Chemistry Definition, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.

Nuclear Chemistry Section 1 Basic Definitions Nuclear Chemistry The Study Of The Atomic Nucleus Its Reactions And Radioactivity Radioactivity Spontaneous Ppt Download Cathedral For Diocese Of Rome
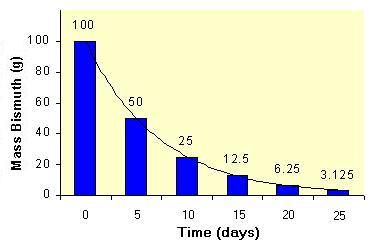
The decay is a nuclear conversion results in a daughter with a different number of protons or neutrons or both.

Cathedral for diocese of rome. Marie curie 1867 1934 was a polish scientist who pioneered research into nuclear radiation figure pageindex1. Radiation chemistry plays a significant role in modern nuclear energy development. The radiation chemistry controls much of radiation biology as radiation has an effect on.
She was awarded the nobel prize in physics in 1903 along with her husband pierre and antoine henri becquerel for their work on radioactivity. Nuclear radiation definition radiation in the form of elementary particles emitted by an atomic nucleus as alpha rays or gamma rays produced by decay of radioactive substances or by nuclear fission. What does nuclear chemistry mean.
Information and translations of nuclear chemistry in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the web. This is very different from radiochemistry as no radioactivity needs to be present in the material which is being chemically changed by the radiation. There are two types of radioactivity sources.
Out of this rule is gamma decay or internal conversion from a nuclear excited state. A combination of radiochemistry and radiation chemistry is used to study nuclear reactions such as fission and fusionsome early evidence for nuclear fission was the formation of a short lived radioisotope of barium which was isolated from neutron irradiated uranium 139 ba with a half life of 83 minutes and 140 ba with a half life of 128 days are major fission products of uranium. Radiation chemistry is a subdivision of nuclear chemistry which is the study of the chemical effects of radiation on matter.
Nuclear radiation refers to the particles and photons emitted during reactions that involve the nucleus of an atomnuclear radiation is also known as ionizing radiation or ionising radiation depending on the country. Natural and artificial as the nuclear reactions inside a reactor.




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-103311355-490ad3ba66d44d40b738a0e7d468ac8a.jpg)