Nuclear Membrane Kills Bacteria What Was The Cold War Like
Nuclear Membrane Kills Bacteria What Was The Cold War Like, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.
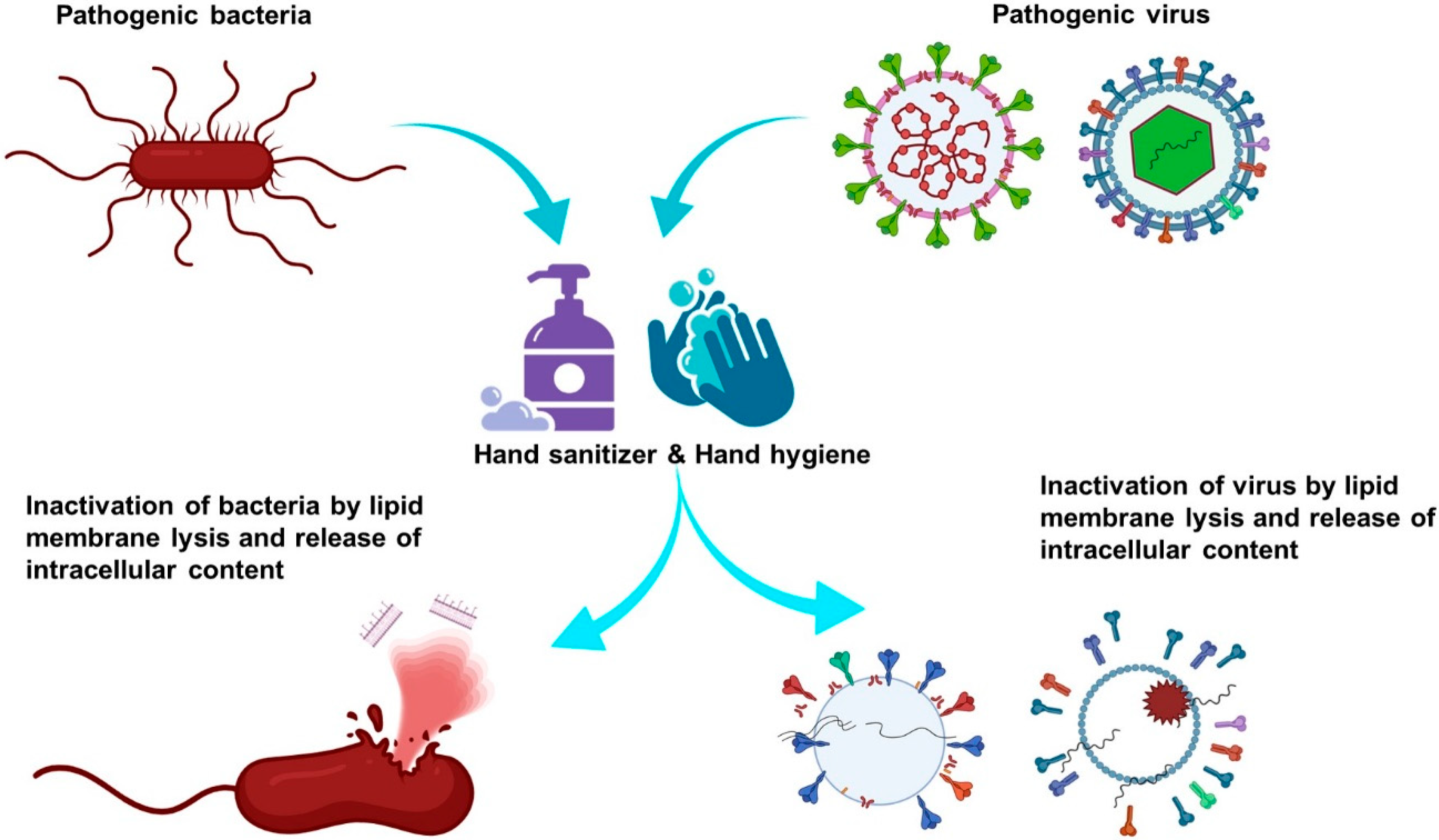
Ijerph Free Full Text Hand Sanitizers A Review On Formulation Aspects Adverse Effects And Regulations Html Nuclear Power What Is It World War Ww2
The cold war may be over but the weapons and geopolitical flashpoints are still there.
Nuclear power what is it world war ww2. It can survive cold dehydration vacuum and acid and therefore is known as a polyextremophile and it has been listed as the worlds toughest known bacterium in the guinness book of world records. Simple cells prokaryotes like bacteria evolved early in the earths history but stayed in that state for over a billion years before evolving into larger more complicated cells eukaryotes. The type of lamins present are a b1 b2 and c.
The lamina acts as a site of attachment for chromosomes. All living organisms on earth are made up of one of two basic types of cells. A membrane surrounds every living cell keeping the cells interior separated and protected from the outside world.
In the post cold war world the global cooling effects of a regional nuclear war could kill more than the conflict itself according to new climate models. The world still possesses around 10000 nuclear. The inner membrane is erected upon the nuclear lamina a network of intermediate filaments made of lamin that plays a role in mitosis and meiosis.
The nuclear envelope may also play a role in the disposition of chromatin inside the nucleus. Why is it so difficult to kill acid fast bacteria. To maintain a fluid plasma membrane in cold conditions bacteria may modify their plasma membranes by.
Eukaryotic cells in which the genetic material is enclosed within a nuclear membrane or prokaryotic cells in which the genetic material is not separated from the rest of the cell. Bristle like structures that extrude from the surface of a prokaryotic cell are called. Acid fast bacteria have mycolic acid in their cell walls which limits drug entry.
Could nuclear war happen sometime in the next 60 years. Deinococcus radiodurans is an extremophilic bacterium and one of the most radiation resistant organisms known. A bacteriophage b ae k t er i o f e d also known informally as a phage f e d is a virus that infects and replicates within bacteria and archaeathe term was derived from bacteria and the greek fagein phagein meaning to devourbacteriophages are composed of proteins that encapsulate a dna or rna genome and may have structures that are either simple.
Chemical and biolgical warfare cbw we now know was a huge danger during the cold war. Biological warfare bw commonly called germ warfare is the use of biological toxins or infectious agents bacteria viruses and fungi to ill or incapacitate people directky or the animals and plants on which people depend.