Nuclear Membrane Genetic Material First World War Wiki
Nuclear Membrane Genetic Material First World War Wiki, Indeed recently has been hunted by consumers around us, perhaps one of you personally. People now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to view video and image information for inspiration, and according to the name of this article I will discuss about
If the posting of this site is beneficial to our suport by spreading article posts of this site to social media marketing accounts which you have such as for example Facebook, Instagram and others or can also bookmark this blog page.
A human cell has genetic material contained in the cell nucleus the nuclear genome and in the mitochondria the mitochondrial genome.

Nuclear power news world war of ship. 2 they contain receptors and channels that allow specific. Since the genetic material has already been duplicated earlier the chromosomes have two sister chromatids bound together at the centromere by a. The outer membrane of the nuclear envelope is continuous with the endoplasmice reticulum er membrane and the lumen of the nuclear envelope is continuous with the lumen of the er.
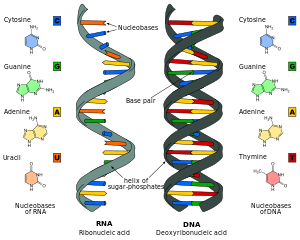
The mitochondrial genome is a circular dna. This will result in the right number of chromosomes 46. In all species it is composed of two helical chains bound to each other by hydrogen bondsboth chains are coiled around the same axis and.
Biological warfare bwalso known as germ warfareis the use of biological toxins or infectious agents such as bacteria viruses insects and fungi with the intent to kill or incapacitate humans animals or plants as an act of war. The outer and inner membranes are separated by lumen. This is called open mitosis found in most multicellular.
Mitosis is the process of chromosome segregation and nuclear division that follows replication of the genetic material in eukaryotic cells. Dna is a long polymer made from repeating units called nucleotides each of which is usually symbolized by a single letter. As human populations moved to different climates and ecosystems taking the crops with them the crops adapted to the new environments developing for example genetic traits providing tolerance to conditions.
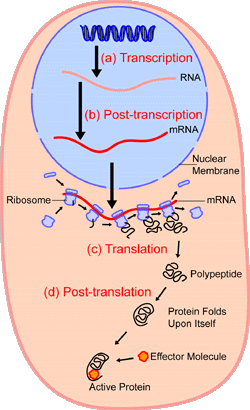
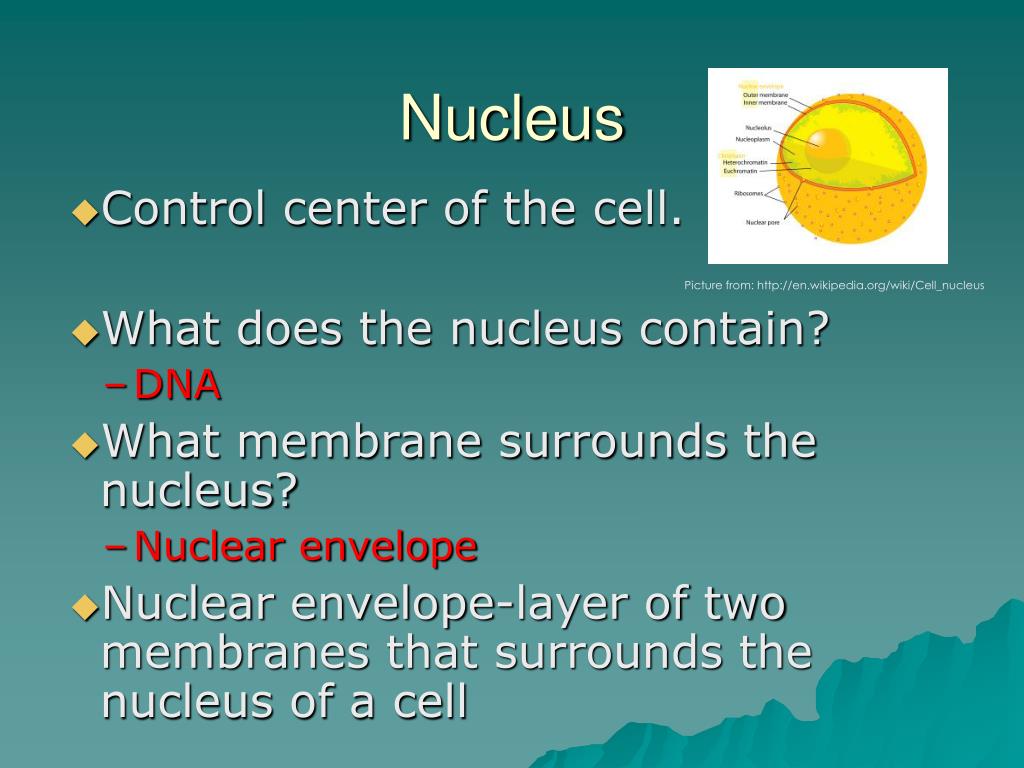
The nuclear envelope completely encloses the nucleus and separates the cells genetic material from the surrounding cytoplasm serving as a barrier to prevent macromolecules from diffusing. The nuclear membrane dissolves in some eukaryotes reforming later once mitosis is complete. The genetic material forms a mass called chromatin that is concentrated in one part of the nucleus.
The nuclear envelope otherwise known as nuclear membrane consists of two cellular membranes an inner and an outer membrane arranged parallel to one another and separated by 10 to 50 nanometres nm. When prophase begins chromatin condenses together into a highly ordered structure called a chromosome. Either a t c or g.
The outer boundary is the plasma membrane and the compartments enclosed by internal membranes are called organellesbiological membranes have three primary functions. Membrane in biology the thin layer that forms the outer boundary of a living cell or of an internal cell compartment. The first use of plant genetic resources dates to more than 10000 years ago when farmers selected from the genetic variation they found in wild plants to develop their crops.
In humans the nuclear genome is divided into 46 linear dna molecules called chromosomes including 22 homologous chromosome pairs and a pair of sex chromosomes. The structure of dna is dynamic along its length being capable of coiling into tight loops and other shapes. Normally the genetic material in the nucleus is in a loosely bundled coil called chromatin.
Meiosis is the process in which a cell reduces its cell from being a diploid having two sets of chromosomes to being a haploid having one set of the twenty three chromosomes when creating eggs and sperm. 1 they keep toxic substances out of the cell.